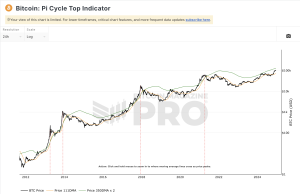
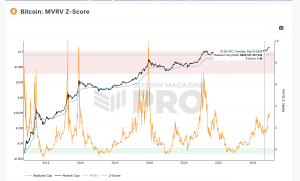
Understanding Bitcoin’s 4 year Cycle
Since its introduction in 2009, Bitcoin has fascinated many with its revolutionary approach to digital currency. Unlike traditional currencies, Bitcoin operates on a cycle of highs and lows, most notably observed in what is referred to as the four-year cycle. This cycle is a fascinating pattern of Bitcoin’s price fluctuations that can be broken down into simpler terms for better understanding.

What is the Four-Year Cycle?
At its core, the four-year cycle of Bitcoin is a pattern in which the price of Bitcoin experiences significant changes over approximately four years. This cycle is closely tied to the process of Bitcoin mining, the method by which transactions are verified and new Bitcoin is created.
Bitcoin mining rewards are halved every 210,000 blocks, a process that takes about four years. As these rewards decrease, the supply of new Bitcoins slows down, potentially increasing demand and, subsequently, the price of Bitcoin. This cycle has historically led to periods of rapid price increase followed by a decrease and then a period of stabilization.
The Phases of the Cycle
- Accumulation Phase: This phase follows a peak and subsequent decline in Bitcoin’s price. It is a period where investors and traders buy Bitcoin at lower prices, anticipating the next surge in value.
- Mark-Up Phase: This phase is marked by a rapid increase in Bitcoin’s price, driven by heightened demand. It usually occurs around the midway point of the four-year cycle.
- Distribution Phase: After reaching a peak, this phase sees investors and traders who bought in the accumulation phase selling their Bitcoin for profit, leading to a price decline.
- Markdown Phase: Characterized by a sharp fall in price, this phase adjusts the market to new supply and demand dynamics. It can last several months or even years.
Strategies to Profit from the Cycle
- Buy and Hold: Buying Bitcoin during the accumulation phase and holding through the cycle can be profitable, given Bitcoin’s long-term price increase trend.
- Swing Trading: This involves buying low during the accumulation phase and selling high during the mark-up phase, using market analysis to guide buying and selling decisions.
- Day Trading: This strategy takes advantage of daily price fluctuations, requiring a keen eye on market trends and news for successful trades.
- Mining: Mining involves validating transactions and creating new blocks, rewarding miners with new Bitcoins and transaction fees, which can then be sold.
Conclusion
Understanding Bitcoin’s four-year cycle offers insight into its price patterns, presenting opportunities for strategic investments. However, it’s crucial to approach Bitcoin investment with caution due to its volatility. Conducting thorough research and consulting with financial experts is advisable before making any investment decisions, ensuring a well-informed approach to navigating the complexities of Bitcoin’s market dynamics.